VMware Cloud Foundation Add Host and Cluster Failed
When adding a host or cluster to VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF), several factors can cause failures. Understanding these potential issues will help troubleshoot and resolve them effectively. Below is a detailed article addressing the common causes and solutions for a failed “Add Host and Cluster” operation in VMware Cloud Foundation.
Common Causes of the Failure
1. Network Configuration Issues
VCF heavily relies on a robust and well-configured network for communication between the hosts and management components. If the host or cluster you are adding has network configuration problems, the process may fail.
- DNS Misconfiguration: Ensure the hosts have proper DNS entries. Reverse and forward DNS lookups should resolve correctly for both the hosts and the management network.
- IP Address Misconfiguration: Check if the IP addresses assigned to the hosts are correct, valid, and reachable from the management cluster.
- VLAN Mismatch: Ensure the VLANs used by the host are configured correctly across all network devices, such as switches.
2. Version Incompatibility
VMware Cloud Foundation supports specific versions of vSphere, ESXi, NSX, and vSAN. If the host you’re adding runs a version incompatible with your current VCF deployment, the operation will fail.
- Check Version Compatibility: Always verify that the ESXi version on the hosts being added matches or is compatible with the existing VMware Cloud Foundation deployment.
- Upgrade Paths: If the versions are incompatible, you may need to upgrade the hosts to the appropriate version before attempting to add them.
3. Host Profile Non-Compliance
When adding hosts to a VCF workload domain, the host profiles must be compliant with the expected settings, including network settings, storage configuration, and security policies.
- Validate Host Profiles: Use the Host Profile Compliance feature to ensure that the new host’s configuration matches the existing cluster. If not, remediate the host profile compliance issues before proceeding.
4. vSAN or Storage Issues
VCF relies on vSAN for its hyper-converged infrastructure. If the new host has issues with vSAN configuration or storage access, the addition will fail.
- Storage Configuration: Ensure that the new host can access the required storage. The vSAN configuration should be consistent across all hosts in the cluster.
- vSAN Disk Groups: Check the disk groups and ensure the host is configured to use vSAN appropriately.
5. Licensing Issues
Each host added to VCF requires appropriate licensing, including licenses for vSphere, vSAN, and NSX (if applicable). If there are insufficient or incorrect licenses applied, the operation will fail.
- Verify Licenses: Ensure you have valid licenses for all components needed to support the new hosts.
6. NSX Configuration Issues
If your VCF deployment uses NSX for networking and security, issues with the NSX configuration can also prevent hosts or clusters from being added successfully.
- NSX-T Compliance: Ensure that the new host is compatible with your NSX deployment and that any transport nodes are correctly configured.
7. Management Domain Resource Constraints
The management domain in VCF should have sufficient resources (CPU, memory, storage) to accommodate additional hosts or clusters. If the management domain is under-provisioned, the process can fail.
- Resource Availability: Check resource availability in the management domain and expand resources if necessary.
Troubleshooting Steps
Follow these steps to troubleshoot the “Add Host and Cluster” failure:
- Verify Network Settings:
- Check the host’s network configuration for connectivity to the management domain.
- Verify that the appropriate VLANs are configured and accessible.
- Use the
pingandnslookupcommands to check the network reachability and DNS resolution.
- Check the vSphere and ESXi Versions:
- Ensure the host ESXi version is compatible with the VCF version.
- Consider upgrading the ESXi version if it’s outdated.
- Host Profile Compliance:
- Compare the new host’s settings against the existing host profiles.
- Correct any non-compliance issues by either updating the host or adjusting the profile.
- Review vSAN Configuration:
- Ensure that the host is properly configured for vSAN and that it has access to the storage cluster.
- Verify disk group configurations for vSAN.
- Review Licensing:
- Ensure the host has appropriate licenses for vSphere, vSAN, NSX, and other VMware services.
- Check NSX Settings:
- Validate the NSX configuration and ensure the new host integrates correctly with NSX if used.
- Check the Logs:
- VMware Cloud Foundation logs will provide detailed error messages.
- Access the logs via the vSphere Web Client or the VCF SDDC Manager to pinpoint the cause of the issue.
Log Locations
In addition to troubleshooting steps, the following log files may provide additional information on the failure:
- vSphere Logs:
/var/log/vmkernel.logand/var/log/vpxa.log - vSAN Logs:
/var/log/vsantraces.log - NSX-T Logs:
/var/log/nsx/
Resolving the Issue
Once the cause is identified, follow the specific remediation path. For instance:
- For network misconfigurations, correct IP, DNS, or VLAN issues.
- For version mismatches, upgrade the ESXi version or VCF components.
- For licensing issues, ensure that you apply the proper VMware licenses.
- If the issue is with storage or vSAN, ensure that vSAN is correctly configured and that the host can access storage resources.
Final Steps: Retrying the Add Host/Cluster Operation
- Retry the Add Host Operation: Attempt to add the host or cluster again through the VCF SDDC Manager.
- Validate: Ensure the new host or cluster is fully operational and integrated into the VCF environment.
Conclusion
Adding hosts or clusters to VMware Cloud Foundation can fail due to various factors, such as network issues, version mismatches, licensing problems, or storage misconfigurations. Identifying and troubleshooting these issues effectively requires checking the logs, ensuring compliance with VMware standards, and resolving any identified conflicts.
By following the above steps, you can troubleshoot and resolve failures encountered during the “Add Host and Cluster” process in VMware Cloud Foundation.
Get eCommerce hosting from Fastdot
The Issue?: Can’t Add Hosts or Clusters to VCF Domains
You’ve done everything right; built resilient data centers using VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Regions, patched both data centers, enabled NSX Federation, and everything is humming along.
Next you need to add / replace an existing host in one of the domains or add a whole new cluster. Typically this is a simple operation, however, you start the process and hit the issue shown in the screenshot below.
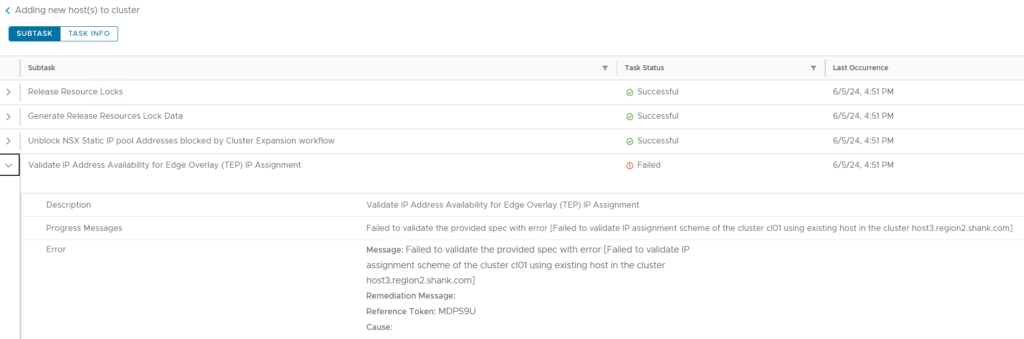
The Issue?
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) introduced NSX Policy API in version 5.1, as part of this shift, certain domain operations use the latest policy API. The issue encountered here (from my testing) was specifically to do with VCF environments that had been federated using NSX Federation. Upon checking the environment, everything else was healthy, passwords were up to date, so there was nothing at surface level that could have been causing the issue.
The Fix!
First up, SSH to SDDC manager, then SU to root, once done, edit the ‘application-prod.properties’ file using VI or your preferred text editor.

Add the following line to the bottom of the file;
nsxt.base.version.policy=4.2.0.0.0-0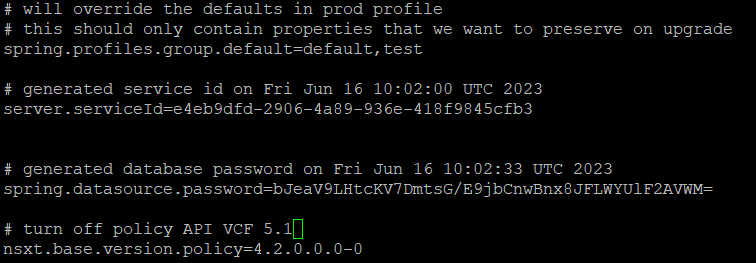
Restart the domain manager service and ensure it is up and running again;
systemctl restart domainmanager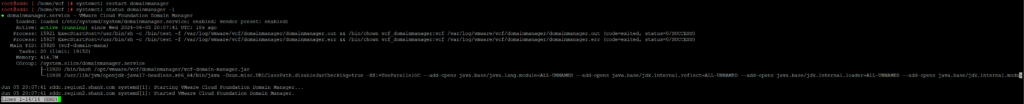
Retry the workflow to add the host or cluster to the domain.
As you can see below, the add new host workflow has now completed successfully, you can comment out the changes you made or leave it there until all your domain add operations are complete. It will not hinder any upgrades in the future.

All this change is doing, is making SDDC Manager use older API’s that have been deprecated, however, are still functional.
You can check out some of my other VCF related articles here and my YouTube channel below.